
8–10 The main disadvantages are erosion of the clinician–patient relationship and concerns around quality of care. 2–7 There is less available evidence from primary care however, there are positive findings in primary care chronic disease management. The reported advantages include lower financial costs, high patient satisfaction, better rural access, decreased waiting times and fewer missed appointment. In this decade, there has been an explosion in telemedicine research, focusing on specific medical specialties. Telemedicine is a recent development within healthcare. This paper will focus on all forms of telemedicine involving direct patient care where the carbon footprint of the telemedicine project is compared to a face-to-face (FTF) scenario. The data may be transmitted via a variety of media, such as audio, video or text. 1 Asynchronous involves sending pre-recorded information between individuals, whereas synchronous is real-time data transmission. The applications of telemedicine can be categorised according to type of interaction (clinician-to-patient or clinician-to-clinician) or timing (asynchronous or synchronous). This paper uses the World Health Organization definition of telemedicine, defined as the use of ICT ‘for the exchange of valid information for diagnosis, treatment and prevention of disease and injuries, research and evaluation, and for the continuing education of health care providers’. The scope of services that fall within the remit of telemedicine is ambiguous. Telemedicine is the use of information and communications technologies (ICT) within the realm of healthcare. In order for telemedicine services to be successfully implemented, further research is necessary to determine context-specific considerations and potential rebound effects. This could have wide implications in reducing the carbon footprint of healthcare services globally.

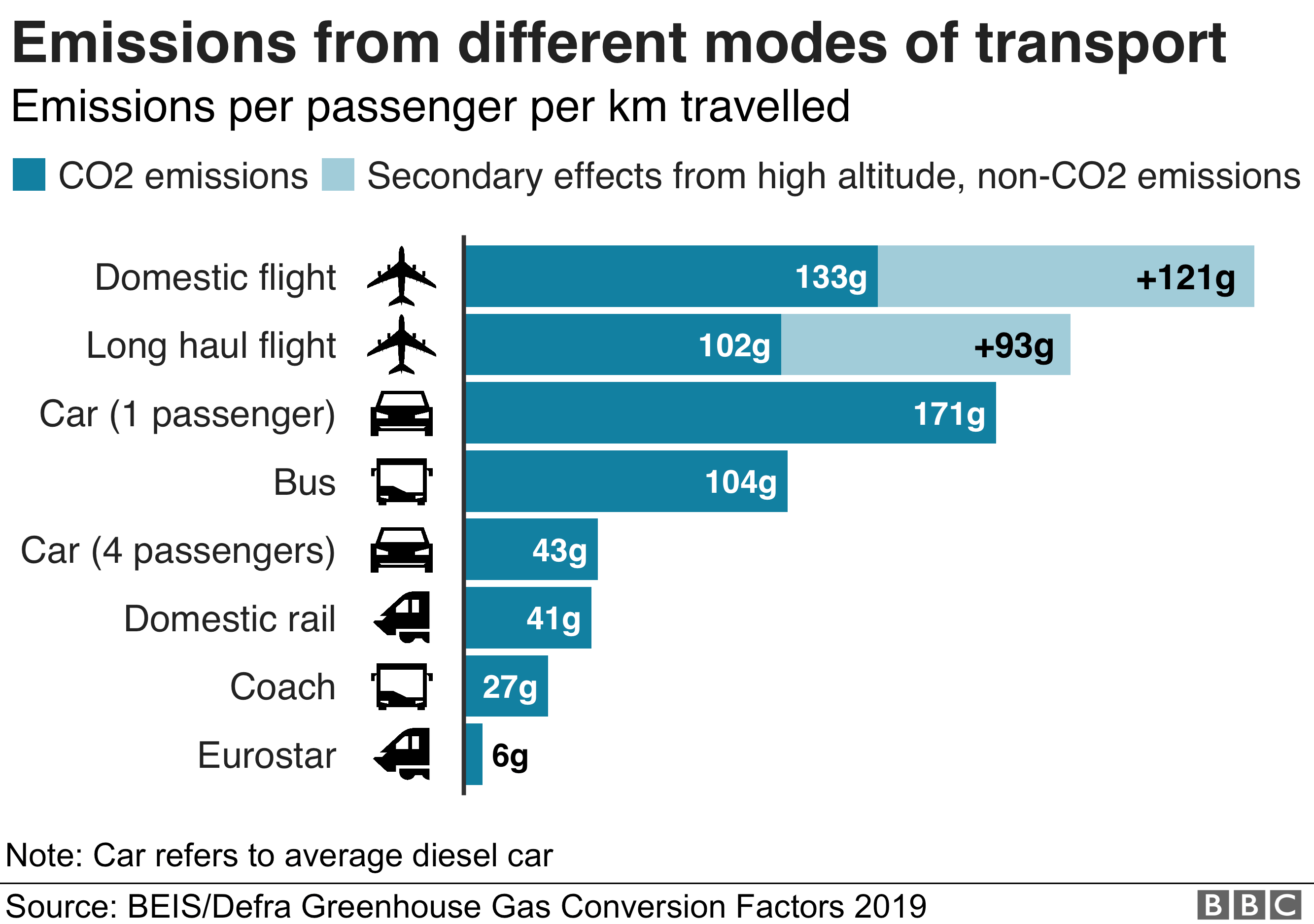
The carbon emissions produced from the use of the telemedicine systems themselves were found to be very low in comparison to emissions saved from travel reductions. However, these values are highly context specific. The carbon footprint savings range between 0.70–372 kg CO 2e per consultation. The identified papers unanimously report that telemedicine does reduce the carbon footprint of healthcare, primarily by reduction in transport-associated emissions. This report provides a systematic review of the evidence on the carbon footprint of telemedicine.
Guardian readers believe it's fairer too.In the rapidly progressing field of telemedicine, there is a multitude of evidence assessing the effectiveness and financial costs of telemedicine projects however, there is very little assessing the environmental impact despite the increasing threat of the climate emergency. Even the former UK deputy prime minister John Prescott recently said that per capita emissions are the fairest way of thrashing out a deal in Copenhagen.
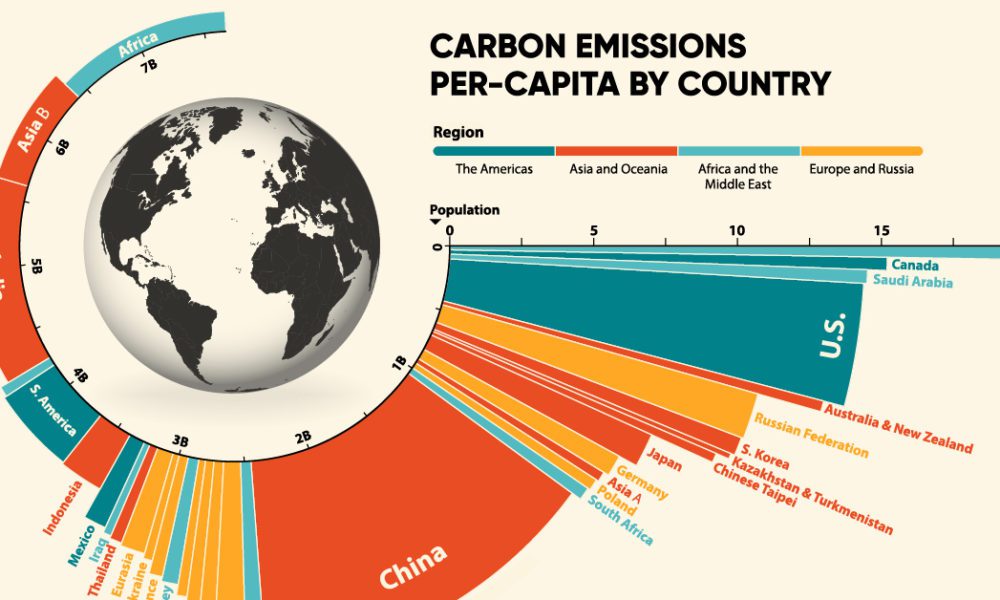
These differences – along with countries' historical contributions to global warming – are a crucial part of climate negotiations in Copenhagen this December. Poorer African nations such as Kenya are on an order magnitude less again – the average Kenyan has a footprint of just 0.3 tonnes (a figure that's likely to drop even lower with the country's surge in wind power). While Australia is on 20.6 tonnes per person (partly because of its reliance on CO2-intensive coal) and the UK is half that at 9.7 (explained in part by relatively CO2-light gas power stations), India is on a mere 1.2. Under that measurement, the average American is responsible for 19.8 tonnes per person, and the average Chinese citizen clocks in at 4.6 tonnes.Įxamining CO2 per capita around the world also shows us the gulf between the developed world's responsibility for climate change and that of the developing world. But all that really tells you is that China is a fast-developing country with a lot of people.Ī more useful measurement is carbon emissions per capita (person).
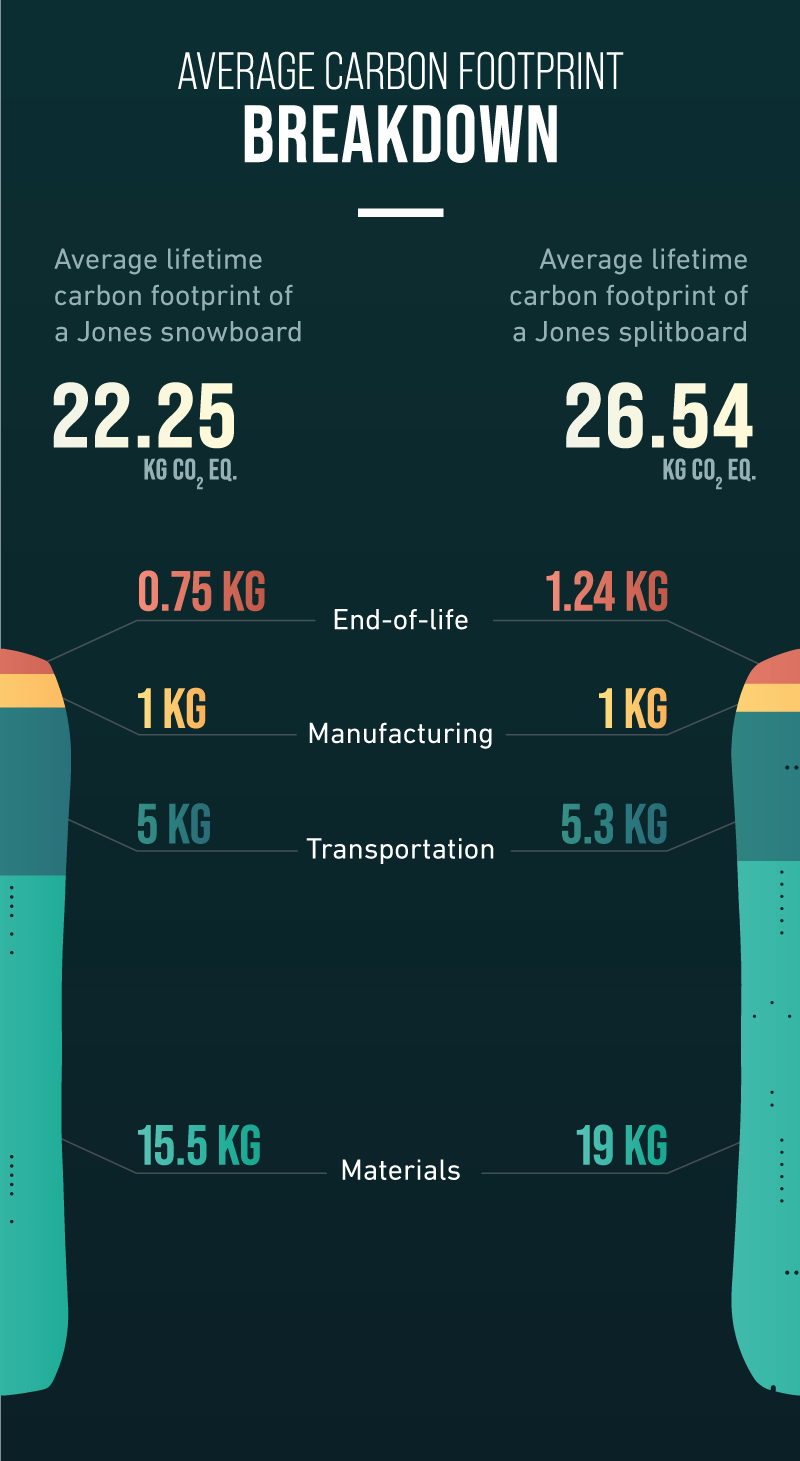
AVERAGE CARBON FOOTPRINT FULL
Looking at a country's total carbon emissions doesn't tell the full story of a country's contribution to global warming.Ĭhina, for example, is the world "leader" in total emissions (6018m metric tonnes of carbon dioxide) since it overtook the US (5903) in 2007.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
